Nigerian-Born Microbiology Researcher, Ahmed Yusuf, Wins Research Excellence Award in United States

By Ishola Lawal
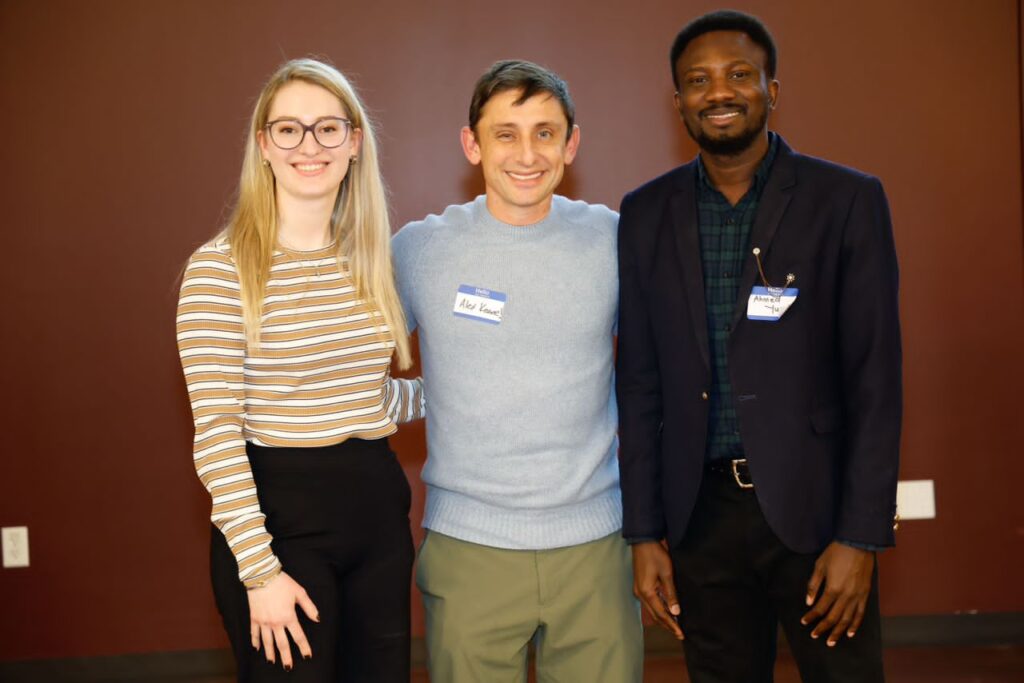
Nigerian-born microbiology researcher Ahmed Yusuf has made history as he wins an award at the Student-Postdoc Research Conference (SPRC) organized by Texas A&M University. At the 2025, SPRC conference, held at the Hildebrand Equine Complex on January 25.
Ahmed Yusuf presented groundbreaking research on developing novel therapeutic solutions to address the rise in antimicrobial resistance caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
His presentation highlighted ongoing research on how to provide alternative treatment options for multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. The SPRC conference attracted approximately 200 participants for research presentation, highlighting its competitiveness.
Ahmed Yusuf earned second place, as judged by field experts serving as moderators. Ahmed Yusuf’s research focuses on developing alternative therapeutic solutions to treat chronic infections caused by multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This pathogen is notorious for rapidly developing resistance to most commercially available antibiotics, leaving patients with limited treatment options.
The World Health Organization (WHO) and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have designated multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a high-priority pathogen requiring urgent intervention. The CDC estimates it costs the U.S. approximately $767 million annually, with 32,600 infections and 2,700 deaths.
Ahmed Yusuf is developing innovative solutions to combat this multidrug-resistant pathogen. Reflecting the significance of his contributions, Yusuf is a key member of a research project funded by the U.S. National Institutes of Health, led by his laboratory. The high prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections, particularly in hospital settings, makes them a critical target for novel interventions. Antivirulence-based approaches, which involve disrupting virulence pathways such as quorum sensing or biofilm formation to reduce pathogenicity, are being explored as alternatives to traditional antibiotics.
These strategies aim to weaken the bacteria’s ability to cause harm, allowing the host immune system to clear the infection with reduced risk of resistance development. Ahmed Yusuf at Texas A&M University is exploring this antivirulence-based approach as an alternative to typical drugs.
According to Texas A&M University’s website, Ahmed Yusuf employs a combination of techniques, including live-cell fluorescence imaging, genetics, molecular tools, and biophysical simulations, to investigate Pseudomonas aeruginosa’s resistance mechanisms and develop novel therapies to bypass established resistance pathways. Ahmed Yusuf’s research is poised to contribute to the growing market for Pseudomonas aeruginosa treatment options, projected to exceed $5.01 billion by 2030.
Ahmed Yusuf’s recognition at the SPRC conference establishes him as a rising voice in microbiology. As the world seeks solutions to antimicrobial resistance to reduce patients’ prolonged hospital stays and the financial burden of managing chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections, researchers like Ahmed demonstrate the impact of groundbreaking research.